Chelation Therapy
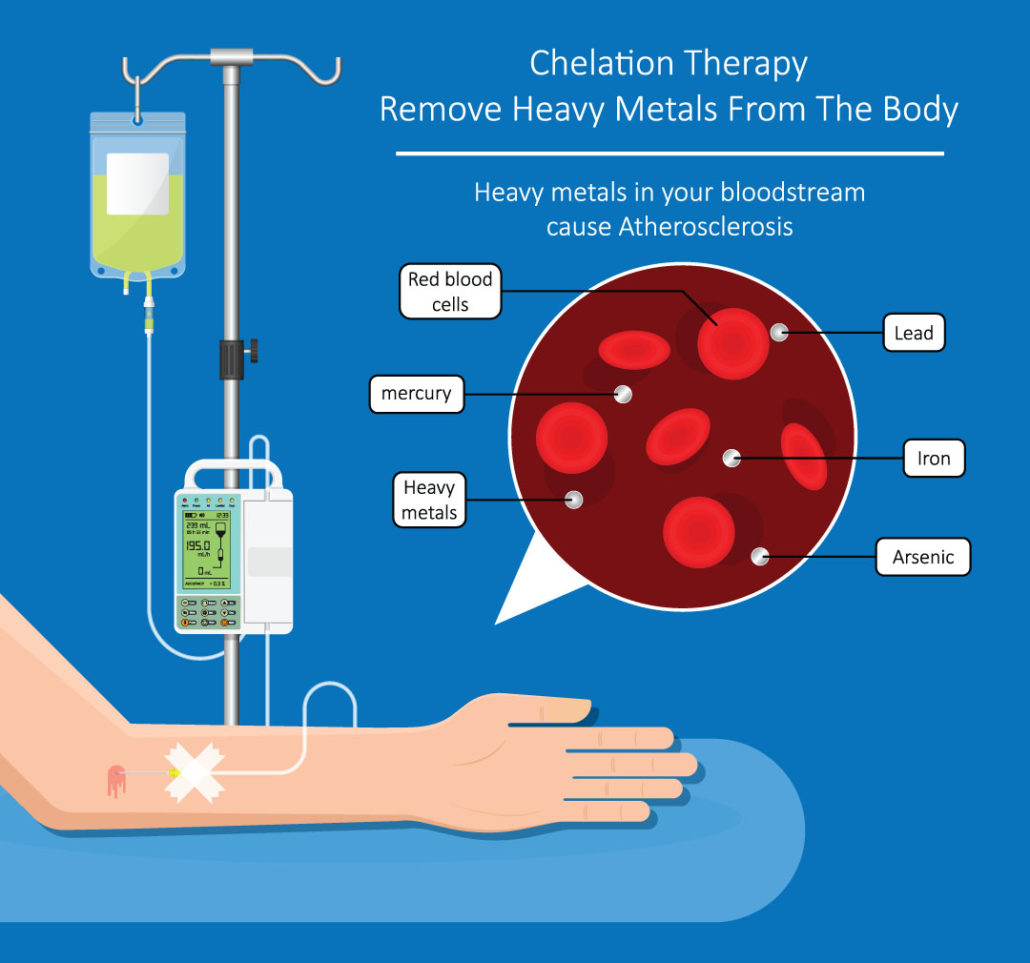
Chelation involves the use of compounds to bind to specific heavy metals and remove them from the body.
Chelation involves the use of compounds to bind to specific heavy metals and remove them from the body.
Chelation therapy (pronounced key-LAY-shun) has been used as a treatment (either oral or intravenous) for removing heavy metals from the blood since the 1950s. Chelation involves the use of compounds to bind to specific heavy metals, including mercury, lead, cadmium, and arsenic, and remove them from the body. It involves intravenous injections of a chelating agent, typically EDTA (ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid), which binds to heavy metals and minerals in the blood so that the body can then eliminate them.
With the expanding use of heavy metals in manufacturing processes, these toxic substances are finding ways into the human body. Heavy metals include single atoms of compounds of the following elements: lead, mercury, iron, copper, manganese, cadmium, arsenic, nickel, aluminum, silver, and beryllium. Heavy metals are extremely toxic to a patient’s body and even a single atom can wreak devastating havoc on cells, organs, neurological functioning, and many other systems of the body. Some heavy metals are more dangerous than others (such as mercury, arguably the most dangerous of the heavy metals).
Today, heavy metal toxicity is a growing problem. For instance, if many people have mercury fillings in their teeth, have been vaccinated, eat farm-raised fish or chicken regularly, consume processed food, or have gone through radiation and chemotherapy treatments, they may be experiencing heavy metal toxicity at this very moment. It is well known that heavy metals are difficult to remove from the system, and chelation therapy may be an excellent alternative to detoxify and restore the body.
Chelation therapy has shown promise in successfully improving the health of patients with such disorders as peripheral vascular disease, Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, autism, and other chronic and complex conditions.
Clinical experience has shown that chelation therapy may be used for a number of conditions and issues and that the benefits include:
Since the Industrial Revolution, the use of heavy metals has greatly escalated. Due to the common practices of using heavy metals in technological devices (lead, mercury, and arsenic are used in microchips and batteries of cell phone) and their prominence in modern agriculture (heavy metals are a major component in inorganic fertilizers and pesticides), as well as increased rates in food supply, heavy metal exposure continues and is increasing in many parts of the world.
Once in the body, heavy metals can have very detrimental effects on numerous systems and organs and are contributing factors to conditions like heart disease, thyroid problems, dementia, neurological and degenerative conditions, autism, infertility and birth defects.
Chelation offers an effective clinical manner to remove heavy metals that otherwise are stored in the kidneys, blood, spleen, brain, liver, bones and fatty tissues. Of the two methods, intravenous chelation is quicker and more effective, as oral chelation involves taking supplements that contain the binding agents over a longer period of time. After administration of the drug into a patient (whether orally or intravenously), the chelating agent works by binding to heavy metal particles and the complex is then removed from the body through normal excretory methods (urination, sweat, etc). The chelating process also removes vital nutrients such as vitamins C and E, so additional supplementation may be necessary while undergoing treatment.
Let’s take a closer look at these methods:
Oral chelation is a safe and effective way for many people to detoxify. Frequently, oral chelators are given to people while intravenous chelations are performed as supplemental and supportive agents to overall detoxification. EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) is a safe oral chelator used by many to detoxify, which will be thoroughly covered in the intravenous section. Other oral chelators include Vitamin C, garlic, cilantro, chlorella, as well as pleomorphic remedies such as Pleo-Chelate. In addition, many people take oral supplements that support and nourish the body and the vital organs while it is going through a detox program. These supplements are also safe to take any time since they are supportive of the body’s natural processes and vital detox organs (liver, kidneys, lymphatic system, etc.). Specialized biological medicines, such as spagyric medicine, can also be very effective for chelation since they support the organs responsible for detoxification.
There are several different types of intravenous chelation. Some provide general detoxification of heavy metals while some are more specific to a certain heavy metal such as lead or mercury. They all involve receiving an I.V. drip (or push) directly into the vein for an extended period of time, usually anywhere from half an hour to 3 hours depending on the chelating agent and desired speed of the drip. The more effective and specific the I.V. drip is, the shorter the time period. Chelation treatment should never be rushed because it does take time for the chelators to be administered into the body and work properly. Before chelation is started, a complete medical workup is performed. Complete chemistry panels for blood, thyroid, kidney, and liver function are standard. The main active chelating agent in intravenous infusions is EDTA (ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid), a synthetic amino acid. EDTA binds to heavy metals and minerals in the blood so that they can be excreted in the urine. The two main types of EDTA are calcium and magnesium; calcium being the more effective in that it doesn’t deplete the body of calcium. Vitamin C is also a powerful chelating agent and used by some doctors. Another intravenous agent used by some physicians for mercury detoxification is called DMPS (2,3-Dimercapto-1-propanesulfonic acid). Along with the chelating agents, certain other nutrients are also introduced in the infusion, used as a “piggyback” to the chelating agent. These include magnesium chloride, ascorbic acid, vitamin B12, B complex, and multi-mineral compounds. This is often done to replenish the body as it flushes out more than just toxins.
In summary, chelation therapy is a chemical process in which a chelating agent is introduced into the bloodstream to help remove heavy metals and toxins from the body. Chelation means “to bind”, and when the chelating agent enters the body, whether intravenously or orally, it binds with heavy metals and toxins such as lead, mercury, copper, iron, arsenic, aluminum, and calcium and the compound that is created is ushered out of the body.
It is advised that practitioners utilize a method of personalization to increase the effectiveness of chelation therapy and avoid side-effects that may come from intensified heavy metal detoxification.
“Published research and extensive clinical experience showed that EDTA helped reduce and prevent arteriosclerotic plaques, thus improving blood flow to the heart and other organs. The scientific evidence indicates that a course of EDTA chelation therapy might eliminate the need for bypass surgery.”
DR. LINUS PAULING, MD, PHD, SCIENTIST, TWO-TIME NOBEL PRIZE WINNER
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) sponsored a study designed to determine the safety and efficacy of EDTA chelation therapy for individuals with prior heart attacks. The goal was to detect if there are any moderate benefits or risks associated with the therapy. The research has shown that 40 infusions of disodium EDTA reduced the risk of some cardiac events in adults who had previously experienced a heart attack.
source: Questions and Answers: The NIH Trials of EDTA Chelation Therapy for Coronary Heart Disease, 2014
Research also shows that chelation therapy can successfully treat neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. While the exact mechanisms in which EDTA helps resolve these problems have not been conducted in studies, there seems to be a connection between heavy metal toxicity, including high levels of mercury or lead, and neurodegenerative disorders that affect the brain, memory and learning.
source: Chelating agents for neurodegenerative diseases, Universite Catholique de Louvain, Belgium 2012
The most common side effect of chelation therapy is a burning sensation at the site where the drug is injected into the vein. When used properly in response to a diagnosis of harm from metal toxicity, side effects of chelation therapy include dehydration, low blood calcium, harm to kidneys, increased enzymes as would be detected in liver function tests, allergic reactions, and lowered levels of dietary elements. Infrequently, reversible kidney injury has been reported. Other serious side effects can occur if EDTA is not administered by a trained health professional.
At the New York Center of Innovative Medicine, chelation therapy is one of many different treatments considered for each patient. However, the use of this therapy is only performed on patients after an in-depth initial evaluation reveals it would be necessary for your personalized program of treatment. Because each person is unique, and their health needs are different, there is no set protocol for using chelation therapy nor is the patient able to request the use of this therapy if the medical team finds it would not be as helpful as another treatment or specific combination of therapies. The ultimate goal is the complete restoration of health in the most efficient and safe manner, and with so many therapeutic options, it is impossible to know if chelation therapy is right for you without an initial evaluation at our clinic.
Contact NYCIM and Book Your Appointment Today
or
» Take Our Questionnaire to See if You’re a Good Candidate
or
» See Additional NYCIM Services & Therapies
Innovative Medicine is about restoring your body and mind’s power to heal itself. Learn how to tap into your unique healing potential by signing up for our newsletter.

 Bioresonance Analysis of Health (B.A.H.)
Bioresonance Analysis of Health (B.A.H.)
Trackbacks & Pingbacks
[…] monitoring of human exposure to heavy metals increased as well as a need for detoxification. Chelation is a detox that cleanses the body of heavy metal build-up using organic molecules that bind to […]
Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!